
Please post the source next time. I spent 2 minutes looking for it: https://chrisdallariva.substack.com/p/when-the-fck-did-we-start-singing
Isn't Angstrom 10^-10 meters? And nanometers 10^-9 meters? So 20A (assuming A = Angstrom) is just 2nm?
Are they trying to say that by moving to this new era, they'll go single digit Angstrom i.e., 0.x nm?
I'm glad you appreciate it! It's always fun digging into kernel internals and learning new things :D
I'm also open to criticism about the writing if you have any.
Operating Systems: Three Easy Pieces by Remzi H. Arpaci-Dusseau & Andrea C. Arpaci-Dusseau (University of Wisconsin-Madison) is an excellent book and used by many universities worldwide. Extremely well written and it's one of the only textbooks I've ever completed from start to end.
It's also completely free: https://pages.cs.wisc.edu/~remzi/OSTEP/
Thanks for cross-posting and tagging me 😄! Perhaps lemmy should push a notification if it's cross-posted.
I needed to add a custom System Request (Sys Req or SysRq) to a linux kernel some time ago. While doing so, I dug deep into how it works and I thought I’d make a quick post about it. Here is a good SuperUser answer about what a SysRq is. You may also know about SysRq via REISUB. This post has three ...

> I needed to add a custom System Request (Sys Req or SysRq) to a linux kernel some time ago. While doing so, I dug deep into how it works and I thought I’d make a quick post about it. Here is a good SuperUser answer about what a SysRq is. You may also know about SysRq via REISUB. This post has three parts: how to raise a SysRq, how SysRq works (looking into kernel code), and how to add your own SysRq.
Disclaimer: This is my website.
No. Fuck this shit. Don't do this.
It's already bad when everyone in this community shoves their distro down potential linux-converts' throats, thereby confusing them even more. Don't tell (or imply to) freshly converted users that they potentially made a wrong choice.
TF do you think they're going to do now? Move to fedora? The commenter above already stated that it was a hassle to install Ubuntu and now you're telling them to change distros already???
Ubuntu is still great... compared to Windows. Sure. It may not hold to your ideals. Compared to other distros, canonical may make some questionable choices. BUT THEY DON'T IMPLEMENT A FUCKING RECALL. So it's fine (for now).
Ubuntu is fine for newcomers. It has a shit ton of support online and you can easily search questions whose answers are likely to be found within the first few results.
So stop shoving distros down people's throats, especially fresh users.
I know you said:
Sorry if I sound too hard... take it with a laugh 😁
It doesn't come across that way. You come off as a gatekeeper.
Are you in Europe? This is a thing I've seen in Europe, but not in other countries.
Thank you, I'll send you an email within a day.
I knew about the "Thour" meme, but still didn't get why the directory turned compressed. My guess is that by licking the lemon, the directory folds in on itself, thus becoming compressed.
Would you consider sending it to Austria? I'd pay shipping charges (if it's within reason lol). If you are, you can send me an email at: sneela-hwelemmy92fd [at] port87.com
Are you planning to scrap the CPU? I may be interested in it as I find faulty hardware fun to experiment on.
You haven't given us much information about the CPU. That is very important when dealing with Machine Check Errors (MCEs).
I've done a bit of work with MCEs and AMD CPUs, so I'll help with understanding what may be going wrong and what you probably can do.
I've done a bit of searching from the microcode & the Dell Wyse thin client that you mentioned. From what I can garner, are you using a Dell Wyse 5060 Thin Client with an AMD steppe Eagle GX-424 [1]? This is my assumption for the rest of this comment.
Machine Check Errors (MCEs) are hard to decipher find out without the right documentation. As far as I can tell from AMD's Data Sheet for the G-Series [2], this CPU belongs to family 16H.
You have two MCEs in your image:
- CPU Core 0, Bank 4: f600000000070f0f
- CPU Core 1, Bank 1: b400000001020103
Now, you can attempt to decipher these with a tool I used some time ago, MCE-Ryzen-Decoder [4]; you may note that the name says Ryzen - this tool only decodes MCEs of Ryzen architectures. However, MCE designs may not change much between families, but I wouldn't bank (pun not intended) on it because it seems that the G-Series are an embedded SOC compared to the Ryzen CPUs which are not. I gave it a shot and the tool spit out that you may have an issue in:
$ python3 run.py 04 f600000000070f0f
Bank: Read-As-Zero (RAZ)
Error: ( 0x7)
$ python3 run.py 01 b400000001020103
Bank: Instruction Fetch Unit (IF)
Error: IC Full Tag Parity Error (TagParity 0x2)
Wouldn't bank (pun intended this time) on it though.
What you can do is to go through the AMD Family 16H's BIOS and Kernel Developer Guide [3] (Section 2.16.1.5 Error Code). From Section 2.16.1.1 Machine Check Registers, it looks like Bank 01 corresponds to the IC (Instruction Cache) and Bank 04 corresponds to the NB (Northbridge). This means that the CPU found issues in the NB in core 0 and the IC in core 1. You can go even further and check what those exact codes decipher to, but I wouldn't put in that much effort - there's not much you can do with that info (maybe the NB, but... too much effort). There are some MSRs that you can read out that correspond to errors of these banks (from Table 86: Registers Commonly Used for Diagnosis), but like I said, there's not much you can do with this info anyway.
Okay, now that the boring part is over (it was fun for me), what can you do? It looks like the CPU is a quad core CPU. I take it to mean that it's 4 cores * 2 SMT threads. If you have access to the linux command line parameters [5], say via GRUB for example, I would try to isolate the two faulty cores we see here: core 0 and core 1. Add isolcpus=0,1 to see the kernel boots. There's a good chance that we see only two CPU cores failing, but others may also be faulty but the errors weren't spit out. It's worth a shot, but it may not work.
Alternatively, you can tell the kernel to disable MCE checks entirely and continue executing; this can be done with the mce=off command line parameter [6] . Beware that this means that you're now willingly running code on a CPU with two cores that have been shown to be faulty (so far). isolcpus will make sure that the kernel doesn't execute any "user" code on those cores unless asked to (via taskset for example)
Apart from this, like others have pointed out, the red dots on the screen aren't a great sign. Maybe you can individually replace defective parts, or maybe you have to buy a new machine entirely. What I told you with this comment is to check whether your CPU still works with 2 SMT threads faulty.
Good luck and I hope you fix your server 🤞.
Edited to add: I have seen MCEs appear due to extremely low/high/fluctuating voltages. As others pointed out, your PSU or other components related to power could be busted.
[4] https://github.com/DimitriFourny/MCE-Ryzen-Decoder
[5] https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/admin-guide/kernel-parameters.html
[6] https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v6.9.2/source/Documentation/arch/x86/x86_64/boot-options.rst
Answered this with a screenshot in this thread:
For those of you still struggling (like me), here's an image:
spoiler

The debug version you compile doesn't affect the code; it just stores more information about symbols. The whole shtick about the debugger replacing instructions with INT3 still happens.
You can validate that the code isn't affected yourself by running objdump on two binaries, one compiled with debug symbols and one without. Otherwise if you're lazy (like me 😄):
https://stackoverflow.com/a/8676610
And for completeness: https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc-14.1.0/gcc/Debugging-Options.html
Excellent question!
Before replacing the instruction with INT 3, the debugger keeps a note of what instruction was at that point in the code. When the CPU encounters INT 3, it hands control to the debugger.
When the debugging operations are done, the debugger replaces the INT 3 with the original instruction and makes the instruction pointer go back one step, thereby ensuring that the original instruction is executed.
Wouldn't happen to be in this post, would it?
Linux Inventor Says He Doesn’t Believe in Crypto
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/INT_(x86_instruction) (scroll down to INT3)
https://stackoverflow.com/a/61946177
The TL;DR is that it's used by debuggers to set a breakpoint in code.
For example, if you're familiar with gdb, one of the simplest ways to make code stop executing at a particular point in the code is to add a breakpoint there.
Gdb replaces the instruction at the breakpoint with 0xCC, which happens to be the opcode for INT 3 --- generate interrupt 3. When the CPU encounters the instruction, it generates interrupt 3, following which the kernel's interrupt handler sends a signal (SIGTRAP) to the debugger. Thus, the debugger will know it's meant to start a debugging loop there.

https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.10002
Abstract (emphasis mine):
> The concept of a 'Ballmer Peak' was first proposed in 2007, postulating that there exists a very specific blood alcohol content which confers superhuman programming ability. More generally, there is a commonly held belief among software engineers that coding is easier and more productive after a few drinks. Using the industry standard for assessment of coding ability, we conducted a search for such a peak and more generally investigated the effect of different amounts of alcohol on performance. We conclusively refute the existence of a specific peak with large magnitude, but with p < 0.001 find that there was a significant positive effect to a low amount of alcohol - slightly less than two drinks - on programming ability.
... I am 100% certain that if they switched to being individually wrapped tomorrow, a complaint about excessive packaging would be one of the top posts here.
You're undeniably right. The best situation would be to not have any wrapping at all... but with the crumb situation, that'd be another top post here :/

I was in a rush and I needed to pick up a quick snack that I could eat during class. I chose these Nature Valley bars which said they had ten bars inside. What I failed to notice is the tiny print at the bottom where it says 5 x 2, i.e., 5 packets with two bars.
Lo and behold when I open a pack during a break, I find two bars inside. I didn't want to eat two bars, just one. You can't even just leave the other fucking bar inside because they create so MANY crumbs. How the fuck are you supposed to seal it???
Stupid-ass deceptive printing got the better of me. It's not the end of the world, just mildly infuriating.
<rant> I use Zotero, a “free, easy-to-use tool to help you collect, organize, annotate, cite, and share research” (from their website). Zotero is based on Firefox and users can install addons from XPI files. I looking to install a DOM-Inspector to Zotero and I subsequently found zotero-inspector on ...

> Upon going to the releases page, I clicked on the xpi file only to see an alert pop up in Firefox:
> “The add-on downloaded from this site could not be installed because it appears to be corrupt.”
> I… don’t know if this should be allowed. It just feels wrong.
If you want to skip the floof and see the settings to tweak on Firefox, go to Settings to Tweak below. Don’t you love how tiny scroll bars have become??? I sure do! A bunch of other people on lemmy totally love it too! Just search for scrollbars on lemmy and you’ll see the amount of love there is i...
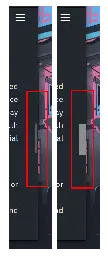
Tl;Dr:
In about:config, I changed these preferences:
- widget.non-native-theme.gtk.scrollbar.round-thumb: false - This makes the scrollbar not have rounded edges
- widget.non-native-theme.gtk.scrollbar.thumb-size: 1 - This makes the scrollbar ‘chonkier’ within the scrollbar region
- widget.non-native-theme.scrollbar.size.override: 20 - This increases the scrollbar region size. Larger number = wider scrollbar
- Make sure widget.gtk.overlay-scrollbars.enabled is set to false - This should have been set to false when you enabled “Always show scrollbars”
On Windows, Firefox follows the system setting (System Settings > Accessibility > Visual Effects > Always show scrollbars).

