I use EndeavourOS and really enjoy it. It’s effectively Arch but without the fuss. You get a GUI with just a few steps to set it up and you’re good to go. I tend to upgrade once a week, while checking the forums to see nothing too bad broke. That’s basically the maintenance I have.
When I do a new install on a new device, I just clone a repo I keep with the most important config files. Then I copy them to where they belong. There’s really not much more to it.
Various ways of using singletons in JavaScript, with their pros and cons
Unfortunately true. I have no solution for the American people. Merely sharing my thoughts to hopefully limit the impact on the democracies that remain.
Using smart pointers doesn’t eliminate the memory safety issue, it merely addresses one aspect of it. Even with smart pointers, nothing is preventing you from passing references and using them after they’re freed.
This is the government's strongest stance yet on software security, which puts manufacturers on notice: fix dangerous coding practices or risk being labeled as negligent.

Would you have a link to that? I know there are many third-party garbage collectors for Rust, but if there’s something semi-official being proposed or prototyped I’d be most curious :)
Cool, that was an informative read!
If we were willing to leak memory, then we could write […]
Box::leak(Box::new(0))
In this example, you could have just made a constant with value 0 and returned a reference to that. It would also have a 'static lifetime and there would be no leaking.
Why does nobody seem to be talking about this?
My guess is that the overlap in use cases between Rust and C# isn’t very large. Many places where Rust is making inroads (kernel and low-level libraries) are places where C# would be automatically disqualified because of the requirements for a runtime and garbage collection.
I think that’s very team/project dependent. I’ve seen it done before indeed, but I’ve never been on a team where it was considered idiomatic.
This does look cool. How would it work together with Steam Input?
I don’t know about your workplace, but if at all possible I would try to find time between tasks to spend on learning. If your company doesn’t have a policy where it is clear that employees have the freedom to learn during company time, try to underestimate your own velocity even more and use the time it leaves for learning.
About 10 years ago I worked for a company where I was performing quite well. Since that meant I finished my tasks early, I could have taken on even more tasks. But I didn’t really tell our scrum master when I finished early. Instead I spent the time learning, and also refactoring code to help me become more productive. This added up, and my efficiency only increased more, until at some point I only needed one or two days to complete a week’s sprint. I didn’t waste my time, but I used it to pick up more architectural stuff on the side, while always learning on the job.
I’ll admit that when I started this route, I already had a bunch of experience under my belt, and this may not be feasible if you have managers breathing down your neck all the time. But the point is, if you play it smart you can use company time to improve yourself and they may even appreciate you for it.
If we’re looking at it from a Rust angle anyway, I think there’s a second reason that OOP often becomes messy, but less so in Rust: Unlimited interior mutability. Rust’s borrow checker may be annoying at times, but it forces you to think about ownership and prevents you from stuffing statefulness where it shouldn’t be.
You can use the regular data structures in java and run into issues with concurrency but you can also use unsafe in rust so it’s a bit of a moot point.
In Java it isn’t always clear when something crosses a thread boundary and when it doesn’t. In Rust, it is very explicit when you’re opting into using unsafe, so I think that’s a very clear distinction.
Java provides classes for thread safe programming, but the language isn’t thread safe. Just like C++ provides containers for improved memory safety, and yet the language isn’t memory safe.
The distinction lies between what’s available in the standard library, and what the language enforces.
Modern C++ does use references, which can also reference memory that is no longer available. Avoiding raw pointers isn’t enough to be memory safe.
Try browsing the list of somewhat recent #CVE rated critical, as I just did to verify. A majority of them is not related to any memory errors. Will you tell all them “just use a different programming language”?
I'm sorry, but this has been repeatedly refuted:
- Google "analysis shows two thirds of 0-day exploits detected in the wild used memory corruption vulnerabilities". Source: https://security.googleblog.com/2024/03/secure-by-design-googles-perspective-on.html
- "Microsoft: 70 percent of all security bugs are memory safety issues" Source: https://www.zdnet.com/article/microsoft-70-percent-of-all-security-bugs-are-memory-safety-issues/
And yes, they are telling their engineers to use a different programming language. In fact, even the NSA is saying exactly that: https://www.nsa.gov/Press-Room/News-Highlights/Article/Article/3215760/nsa-releases-guidance-on-how-to-protect-against-software-memory-safety-issues/
It doesn’t come out today, it’s been there for a long time, and it’s standardized, proven and stable.
This seems like an extremely short-sighted red herring. C has so many gaps in its specification, because it has no problem defining things as "undefined behavior" or "implementation defined", that the standard is essentially useless for kernel-level programming. The Linux kernel is written in C and used to only build with GCC. Now it builds with GCC and LLVM, and it relies on many non-standard compiler extensions for each. The effort to add support for LLVM took them 10 years. That's 10 years for a migration from C to C. Ask yourself: how is that possible if the language is so well standardized?
Great suggestions! One nitpick:
But in principle I find this quite workable, as you get to write your CI code in Rust.
Having used xtask in the past, I’d say this is a downside. CI code is tedious enough to debug as it is, and slowing down the cycle by adding Rust compilation into the mix was a horrible experience. To add, CI is a unique environment where Rust’s focus on correctness isn’t very valuable, since it’s an isolated, project-specific environment anyway.
I’d rather use Deno or indeed just for that.
No, OP asked for a black and white winner. I was elaborating because I don’t think it’s that black and white, but if you want a singular answer I think it should be clear: Rust.
I would say at this point in time it’s clearly decided that Rust will be part of the future. Maybe there’s a meaningful place for Zig too, but that’s the only part that’s too early to tell.
If you think Zig still has a chance at overtaking Rust though, that’s very much wishful thinking. Zig isn’t memory safe, so any areas where security is paramount are out of reach for it. The industry isn’t going back in that direction.
I actually think Zig might still have a chance in game development, and maybe in specialized areas where Rust’s borrow checker cannot really help anyway, such as JIT compilers.
Runtime performance is entirely unaffected by the use of macros. It can have a negative impact on compile-time performance though, if you overdo it.
Might be relevant to mention that Rust has formal verification methods available as well, similar to SPARK, but also optional. One that looks pretty appealing is this one: https://verus-lang.github.io/verus/guide/overview.html
While I can get behind most of the advice here, I don’t actually like the conditions array. The reason being that each condition function now needs additional conditions to make sure it doesn’t overlap with the other condition functions. This was much more elegantly handled by the else clauses, since adding another condition to the array has now become a puzzle to verify the conditions remain non-overlapping.
Today the Direct3D and HLSL teams are excited to share some insight into the next big step for GPU programmability. Once Shader Model 7 is released, DirectX 12 will accept shaders compiled to SPIR-V™. The HLSL team is committed to open development processes and collaborating with The Khronos® Group ...

SPIR-V is the intermediate shader target used by Vulkan as well, so it sounds like this may indirectly make DirectX on Linux smoother.
First anniversary of Biome and release of Biome 1.9 that enables CSS and GraphQL formatting and linting by default, a new search command

Biome v1.9 is out!
Today we celebrate both the first anniversary of Biome 🎊 and the release of Biome v1.9! Read our blog post for a look back at the first year and the new features of Biome v1.9.
In a nutshell:
- Stable CSS formatting and linting. Enabled by default!
- Stable GraphQL formatting and linting. Enabled by default!
.editorconfigsupport. Opt-inbiome searchcommand to search for patterns in your source code.- New lint rules for JavaScript and its dialects.
Async Rust is powerful. And it can be a pain to work with (and learn). Async Rust can be a pleasure to work with, though, if we can do it without `Send + Sync + 'static`.

Practical tips that allow you to build an evolving architecture
With this post I've taken a bit more of a practical turn compared to previous Post-Architecture posts: It's more aimed at providing guidance to keep (early) architecture as simple as possible. Let me know what you think!
On the implications of defining the architecture after you build the product -- part II
After my previous post introducing Post-Architecture, I received a bunch of positive feedback, as well as enquiries from people wanting to know more. So I figured a follow-up was in order. Feel free to ask questions here as well as on Mastodon!
On the implications of defining the architecture after you build the product
This post highlights my experience working with software architecture in startup environments. I think the approach is different enough from the traditional notion of software architecture that it may warrant its own term: post-architecture.
cross-posted from: https://programming.dev/post/12807878
> This new version provides an easy path to migrate from ESLint and Prettier. It also introduces machine-readable reports for the formatter and the linter, new linter rules, and many fixes.
This new version provides an easy path to migrate from ESLint and Prettier. It also introduces machine-readable reports for the formatter and the linter, new linter rules, and many fixes.
I just had a random thought: a common pattern in Rust is to things such as:
rs let vec_a: Vec<String> = /* ... */; let vec_b: Vec<String> = vec_a.into_iter().filter(some_filter).collect();
Usually, we need to be aware of the fact that Iterator::collect() allocates for the container we are collecting into. But in the snippet above, we've consumed a container of the same type. And since Rust has full ownership of the vector, in theory the memory allocated by vec_a could be reused to store the collected results of vec_b, meaning everything could be done in-place and no additional allocation is necessary.
It's a highly specific optimization though, so I wonder if such a thing has been implemented in the Rust compiler. Anybody who has an idea about this?
It's been almost two months since I originally proposed integrating GritQL into Biome. Since then a lot has happened. And a lot more remains to be done. With this post I hope to give a little bit o...

Just a progress update on a fun open-source project I'm involved with. Biome.js is a web toolchain written in Rust, and it provides a great excuse to play around with parsing technologies and other fun challenges :)

Slide with text: “Rust teams at Google are as productive as ones using Go, and more than twice as productive as teams using C++.”
In small print it says the data is collected over 2022 and 2023.
I have a fun one, where the compiler says I have an unused lifetime parameter, except it's clearly used. It feels almost like a compiler error, though I'm probably overlooking something? Who can see the mistake?
main.rs ```rs trait Context<'a> { fn name(&'a self) -> &'a str; }
type Func<'a, C: Context<'a>> = dyn Fn(C);
pub struct BuiltInFunction<'a, C: Context<'a>> { pub(crate) func: Box<Func<'a, C>>, } ```
```text
error[E0392]: parameter 'a is never used
--> src/main.rs:7:28
|
7 | pub struct BuiltInFunction<'a, C: Context<'a>> {
| ^^ unused parameter
|
= help: consider removing 'a, referring to it in a field, or using a marker such as PhantomData
For more information about this error, try rustc --explain E0392.
error: could not compile lifetime-test (bin "lifetime-test") due to 1 previous error
```
A little trick that can help make switch statements more type-safe
Today I'm sharing a little trick that I like to use to make switch statements cleaner and more type-safe. Happy to hear other ideas!
This post explores how we improved upon Bevy's out-of-the-box UI experience for our Sudoku Pi project
As part of my Sudoku Pi project, I’ve been experimenting with improving the Bevy UI experience. I’ve collected most of my thoughts on this topic in this post.
How Fiberplane Notebooks implement Operational Transformation
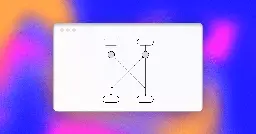
I wrote a post about how our Operational Transfomation (OT) algorithm works at Fiberplane. OT is an algorithm that enables real-time collaboration, and I also built and designed our implementation. So if you have any questions, I'd be happy to answer them!



