Hopefully being a paid app developed full-time by FUTO allows it to be worked on for a long time to come.
I haven't had the exact problem you're describing but I have torn my meniscus playing soccer, which leads to similar problems. I would strongly recommend against taking shortcuts during treatment. I found it to be a recurring problem when I was initially trying to get back to playing and to be honest I can still have little lock-ups even today (three years later) if I am not careful. A professional soccer player at my local club was out for fourteen months with a recurring meniscus injury - he re-tore it twice just straight line running during his recovery and ended up needing three surgeries in total. Knee cartilage injuries shouldn't be underestimated just because they're not the dreaded ACL tear. Often the long-term recovery can be more complicated than a ligament tear.
I recommend taking the recovery slow and easy and working with a physio to build strength around the knee and hips (hip strength will improve your stability and reduce load on the knee). You will lose muscle mass during the recovery period, leaving the knee exposed to re-injury. Personally I chose to give up on returning to soccer due to the potential risk involved and transitioned into long-distance running instead, but it sounds like you're not doing anything that extreme so hopefully you won't experience any long-term restrictions following surgery and rehab.
Yeah, LineageOS can definitely help a lot. I have a Redmi Note 4X from 2017 with 3 GB RAM and a Snapdragon 625. It was fine running an older version of MIUI despite being a budget phone, but after switching to LineageOS it runs even better. But to be honest you don't even need a lighter ROM like LineageOS if the phone was a good one at release. I also have a Galaxy Note 9 from 2018 which is running stock and that still feels great despite how heavy OneUI is. Often these older devices just need a reset to clear out all the junk that accumulates over years of use.
I think the questions over whether some newer phones can handle five or even seven Android version upgrades are valid, since that has never been attempted before (though I still like to see those commitments). But that is very different to saying every phone until now has magically turned terrible after 4 years, when it's likely only running a version of Android that is, at most, two above what it started with.
Nice try, but that's a) a dogshit budget phone and b) one that is 8 years old, not 4.
That's not what you said originally:
unoptimized software starts crippling phones after 4 years
So you admit that age is not actually the relevant factor here? Your complaint is bad updates, not the age of a device. And if bad updates are the problem, which you admitted they aren't for you when you said you'd "never used a phone long enough for this to matter" then your claim that replaceable batteries are irrelevant is also nonsensical. It's as I suspected: you've concocted some weird fictional narrative as a coping mechanism for the cognitive dissonance that comes with repeatedly replacing phones that are absolutely fine.
The OnePlus 12 was released less than a year ago. It has 3 1/2 years of software changes ahead of it. You are proving my point here by implying a 7 month old phone needs to be replaced after a single bad update.
People lie to themselves all the time to justify wasteful consumerism.
Changable batteries, maybe, for the environment. But I've never used a phone long enough for this to matter because unoptimized software starts crippling phones after 4 years anyway.
This is absolute bollocks. Unless you are buying dogshit budget phones, they all continue to run fine after 4 years. I have phones from 2017 and 2018 that continue to operate without major issue today. Until very recently most Android phones weren't even receiving feature updates beyond 4 years so I suspect you've just completely fabricated this story to justify your upgrades.
It's a point of difference in a segment of the market where phones are often thick and heavy.
Yeah, it's a massive overreaction but that's the nature of the Olympics. People are so high on the patriotism during this period, the entire country turns into a cringe circlejerk. Swimming is always the worst offender and has the most toxic culture around it because it's the sport we perform the best in.
Yeah apparently, though I'm not sure if that really matters beyond bragging rights.
I don't think the band broke up, they'll just take a break during the rest of the election cycle. No point continuing to perform when the crazies are sending you death threats.
Possibly, it depends how different the new OS is and whether it's lighter. Check the XDA Developers forum for your phone.
One of my old roomates always used Mitani but he ran out one night so I offered him some of mine and he said he much preferred the nice N tasty and bought some the next day. But his container looked like it was about 5 years old, so maybe by the time he finished it, the moisture had fucked up the taste or the taste had degraded or something.
Mitani chicken salt clumps up after a few years. Turns into this ball you have to shake the fuck out of to get some salt lol
Mitani is South Australian owned and made so I buy that. It tastes good enough to have never bothered trying a non-local alternative.
The AFL CEO wants to see the jiggle physics in-person.
We’re a collective of individuals upset with the way social media has been traditionally governed. A severe lack of moderation has led to major platforms like Facebook to turn into political machinery focused on disinformation campaigns as a way to make profit off of users.
Rules for thee, but not for me?
The pocket comparison is the money shot in that video. So satisfying, particularly as I use a flip phone with a smaller pocket profile so I know exactly how good that reduction in size feels on a daily basis.
Why build Proton Wallet?
Early in our journey, we experienced first-hand what it’s like being cut off from the financial system and at the mercy of large banks and institutions — an ordeal that affects millions of people across the globe. In the summer of 2014, as the original Proton Mail crowdfunding campaign was in progress, Proton had a near-death experience when PayPal froze our funds(new window), questioned whether encryption was legal, and whether Proton had government approval to encrypt emails.
Fortunately, in that instance PayPal returned the blocked funds, and Proton was able to start the journey that we’ve been on for the past decade. However, that dangerous moment has always stayed in our minds, and we still keep a proportion of Proton’s financial reserves in Bitcoin.
Having experienced firsthand the unreliability of the traditional financial sector, building Proton Wallet is an important strategic move to make Proton more resilient and independent in the future. By enabling us and the entire Proton community to more easily adopt means of payment that deliver on the promise of financial freedom for all, we better insulate Proton from the risks posed by traditional finance.
Based Kvaesitso user.
ABC NEWS is Australia’s No 1 online news brand with almost 12.6 million unique visitors in June, according to the latest Ipsos iris data released today*.
Thoughts on the redesign? I'm not sure how I feel about it yet but I didn't particularly like the old design so I don't mind something new. It looks a lot more conventional now, similar to major news outlets like The New York Times, Reuters, Associated Press, etc.
Former prime minister Kevin Rudd has demanded Jack Black 'grow up and get a decent job', following calls from a supposed 'free speech' senator. Politics in 2024 is quite something.

The joke was dumb, the online reaction to the joke was dumb, a random UAP senator's dumb comments being quoted globally was dumb and Rudd telling famous musicians and actors to "grow up and get a job" was very dumb. What a time we live in.
“While these uses of GenAI are often neither overtly malicious nor explicitly violate these tools’ content policies or terms of services, their potential for harm is significant.”

The most common vapes on the market are single-use, disposable ones. They contain valuable resources, yet aren’t designed to be recycled.

'Eritreans have cycling in our blood and know a lot about the Tour de France so to win today was amazing'

EF Education-Easypost terminated the Italian's contract with immediate effect after he was reportedly stopped at an airport and found with the banned substance.

Facebook has been overrun with AI spam and scams. Experts say Facebook has stopped asking them for help.

In spring, 2018, Mark Zuckerberg invited more than a dozen professors and academics to a series of dinners at his home to discuss how Facebook could better keep its platforms safe from election disinformation, violent content, child sexual abuse material, and hate speech. Alongside these secret meetings, Facebook was regularly making pronouncements that it was spending hundreds of millions of dollars and hiring thousands of human content moderators to make its platforms safer. After Facebook was widely blamed for the rise of “fake news” that supposedly helped Trump win the 2016 election, Facebook repeatedly brought in reporters to examine its election “war room” and explained what it was doing to police its platform, which famously included a new “Oversight Board,” a sort of Supreme Court for hard Facebook decisions.
At the time, Joseph and I published a deep dive into how Facebook does content moderation, an astoundingly difficult task considering the scale of Facebook’s userbase, the differing countries and legal regimes it operates under, and the dizzying array of borderline cases it would need to make policies for and litigate against. As part of that article, I went to Facebook’s Menlo Park headquarters and had a series of on-the-record interviews with policymakers and executives about how important content moderation is and how seriously the company takes it. In 2018, Zuckerberg published a manifesto stating that “the most important thing we at Facebook can do is develop the social infrastructure to build a global community,” and that one of the most important aspects of this would be to “build a safe community that prevents harm [and] helps during crisis” and to build an “informed community” and an “inclusive community.”
Several years later, Facebook has been overrun by AI-generated spam and outright scams. Many of the “people” engaging with this content are bots who themselves spam the platform. Porn and nonconsensual imagery is easy to find on Facebook and Instagram. We have reported endlessly on the proliferation of paid advertisements for drugs, stolen credit cards, hacked accounts, and ads for electricians and roofers who appear to be soliciting potential customers with sex work. Its own verified influencers have their bodies regularly stolen by “AI influencers” in the service of promoting OnlyFans pages also full of stolen content.
Meta still regularly publishes updates that explain what it is doing to keep its platforms safe. In April, it launched “new tools to help protect against extortion and intimate image abuse” and in February it explained how it was “helping teens avoid sextortion scams” and that it would begin “labeling AI-generated images on Facebook, Instagram, and Threads,” though the overwhelming majority of AI-generated images on the platform are still not labeled. Meta also still publishes a “Community Standards Enforcement Report,” where it explains things like “in August 2023 alone, we disabled more than 500,000 accounts for violating our child sexual exploitation policies.” There are still people working on content moderation at Meta. But experts I spoke to who once had great insight into how Facebook makes its decisions say that they no longer know what is happening at the platform, and I’ve repeatedly found entire communities dedicated to posting porn, grotesque AI, spam, and scams operating openly on the platform.
Meta now at best inconsistently responds to our questions about these problems, and has declined repeated requests for on-the-record interviews for this and other investigations. Several of the professors who used to consult directly or indirectly with the company say they have not engaged with Meta in years. Some of the people I spoke to said that they are unsure whether their previous contacts still work at the company or, if they do, what they are doing there. Others have switched their academic focus after years of feeling ignored or harassed by right-wing activists who have accused them of being people who just want to censor the internet.
Meanwhile, several groups that have done very important research on content moderation are falling apart or being actively targeted by critics. Last week, Platformer reported that the Stanford Internet Observatory, which runs the Journal of Online Trust & Safety is “being dismantled” and that several key researchers, including Renee DiResta, who did critical work on Facebook’s AI spam problem, have left. In a statement, the Stanford Internet Observatory said “Stanford has not shut down or dismantled SIO as a result of outside pressure. SIO does, however, face funding challenges as its founding grants will soon be exhausted.” (Stanford has an endowment of $36 billion.)
Following her departure, DiResta wrote for The Atlantic that conspiracy theorists regularly claim she is a CIA shill and one of the leaders of a “Censorship Industrial Complex.” Media Matters is being sued by Elon Musk for pointing out that ads for major brands were appearing next to antisemitic and pro-Nazi content on Twitter and recently had to do mass layoffs.
“You go from having dinner at Zuckerberg’s house to them being like, yeah, we don’t need you anymore,” Danielle Citron, a professor at the University of Virginia’s School of Law who previously consulted with Facebook on trust and safety issues, told me. “So yeah, it’s disheartening.”
It is not a good time to be in the content moderation industry. Republicans and the right wing of American politics more broadly see this as a deserved reckoning for liberal leaning, California-based social media companies that have taken away their free speech. Elon Musk bought an entire social media platform in part to dismantle its content moderation team and its rules. And yet, what we are seeing on Facebook is not a free speech heaven. It is a zombified platform full of bots, scammers, malware, bloated features, horrific AI-generated images, abandoned accounts, and dead people that has become a laughing stock on other platforms. Meta has fucked around with Facebook, and now it is finding out.
“I believe we're in a time of experimentation where platforms are willing to gamble and roll the dice and say, ‘How little content moderation can we get away with?,'” Sarah T. Roberts, a UCLA professor and author of Behind the Screen: Content Moderation in the Shadows of Social Media, told me.
In November, Elon Musk sat on stage with a New York Times reporter, and was asked about the Media Matters report that caused several major companies to pull advertising from X: “I hope they stop. Don’t advertise,” Musk said. “If somebody is going to try to blackmail me with advertising, blackmail me with money, go fuck yourself. Go fuck yourself. Is that clear? I hope it is.”
There was a brief moment last year where many large companies pulled advertising from X, ostensibly because they did not want their brands associated with antisemitic or white nationalist content and did not want to be associated with Musk, who has not only allowed this type of content but has often espoused it himself. But X has told employees that 65 percent of advertisers have returned to the platform, and the death of X has thus far been greatly exaggerated. Musk spent much of last week doing damage control, and X’s revenue is down significantly, according to Bloomberg. But the comments did not fully tank the platform, and Musk continues to float it with his enormous wealth.
This was an important moment not just for X, but for other social media companies, too. In order for Meta’s platforms to be seen as a safer alternative for advertisers, Zuckerberg had to meet the extremely low bar of “not overtly platforming Nazis” and “didn’t tell advertisers to ‘go fuck yourself.’”
UCLA’s Roberts has always argued that content moderation is about keeping platforms that make almost all of their money on advertising “brand safe” for those advertisers, not about keeping their users “safe” or censoring content. Musk’s apology tour has highlighted Roberts’s point that content moderation is for advertisers, not users.
“After he said ‘Go fuck yourself,’ Meta can just kind of sit back and let the ball roll downhill toward Musk,” Roberts said. “And any backlash there has been to those brands or to X has been very fleeting. Companies keep coming back and are advertising on all of these sites, so there have been no consequences.”
Meta’s content moderation workforce, which it once talked endlessly about, is now rarely discussed publicly by the company (Accenture was at one point making $500 million a year from its Meta content moderation contract). Meta did not answer a series of detailed questions for this piece, including ones about its relationship with academia, its philosophical approach to content moderation, and what it thinks of AI spam and scams, or if there has been a shift in its overall content moderation strategy. It also declined a request to make anyone on its trust and safety teams available for an on-the-record interview. It did say, however, that it has many more human content moderators today than it did in 2018.
“The truth is we have only invested more in the content moderation and trust and safety spaces,” a Meta spokesperson said. “We have around 40,000 people globally working on safety and security today, compared to 20,000 in 2018.”
Roberts said content moderation is expensive, and that, after years of speaking about the topic openly, perhaps Meta now believes it is better to operate primarily under the radar.
“Content moderation, from the perspective of the C-suite, is considered to be a cost center, and they see no financial upside in providing that service. They’re not compelled by the obvious and true argument that, over the long term, having a hospitable platform is going to engender users who come on and stay for a longer period of time in aggregate,” Roberts said. “And so I think [Meta] has reverted to secrecy around these matters because it suits them to be able to do whatever they want, including ramping back up if there’s a need, or, you know, abdicating their responsibilities by diminishing the teams they may have once had. The whole point of having offshore, third-party contractors is they can spin these teams up and spin them down pretty much with a phone call.”
Roberts added “I personally haven’t heard from Facebook in probably four years.”
Citron, who worked directly with Facebook on nonconsensual imagery being shared on the platform and system that automatically flags nonconsensual intimate imagery and CSAM based on a hash database of abusive images, which was adopted by Facebook and then YouTube, said that what happened to Facebook is “definitely devastating.”
“There was a period where they understood the issue, and it was very rewarding to see the hash database adopted, like, ‘We have this possible technological way to address a very serious social problem,’” she said. “And now I have not worked with Facebook in any meaningful way since 2018. We’ve seen the dismantling of content moderation teams [not just at Meta] but at Twitch, too. I worked with Twitch and then I didn’t work with Twitch. My people got fired in April.”
“There was a period of time where companies were quite concerned that their content moderation decisions would have consequences. But those consequences have not materialized. X shows that the PR loss leading to advertisers fleeing is temporary,” Citron added. “It’s an experiment. It’s like ‘What happens when you don’t have content moderation?’ If the answer is, ‘You have a little bit of a backlash, but it’s temporary and it all comes back,’ well, you know what the answer is? You don’t have to do anything. 100 percent.”
I told everyone I spoke to that, anecdotally, it felt to me like Facebook has become a disastrous, zombified cesspool. All of the researchers I spoke to said that this is not just a vibe.
“It’s not anecdotal, it’s a fact,” Citron said. In November, she published a paper in the Yale Law Journal about women who have faced gendered abuse and sexual harassment in Meta’s Horizon Worlds virtual reality platform, which found the the company is ignoring user reports and expects the targets of this abuse to simply use a “personal boundary” feature to ignore it. The paper notes that “Meta is following the nonrecognition playbook in refusing to address sexual harassment on its VR platforms in a meaningful manner.”
“The response from leadership was like ‘Well, we can’t do anything,’” Citron said. “But having worked with them since 2010, it’s like ‘You know you can do something!’ The idea that they think that this is a hard problem given that people are actually reporting this to them, it’s gobsmacking to me.”
Another researcher I spoke to, who I am not naming because they have been subjected to harassment for their work, said “I also have very little visibility into what’s happening at Facebook around content moderation these days. I’m honestly not sure who does have that visibility at the moment. And perhaps both of these are at least partially explained by the political backlash against moderation and researchers in this space.” Another researcher said “it’s a shitshow seeing what’s happening to Facebook. I don’t know if my contacts on the moderation teams are even still there at this point.” A third said Facebook did not respond to their emails anymore.
Not all of this can be explained by Elon Musk or by direct political backlash from the right. The existence of Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act means that social media platforms have wide latitude to do nothing. And, perhaps more importantly, two state-level lawsuits that have made their way to the Supreme Court that allege social media censorship means that Meta and other social media platforms may be calculating that they could be putting themselves at more risk if they do content moderation. The Supreme Court’s decision on these cases is expected later this week.
The reason I have been so interested in what is happening on Facebook right now is not because I am particularly offended by the content I see there. It’s because Facebook’s present—a dying, decaying, colossus taken over by AI content and more or less left to rot by its owner—feels like the future, or the inevitable outcome, of other social platforms and of an AI-dominated internet. I have been likening zombie Facebook to a dead mall. There are people there, but they don’t know why, and most of what’s being shown to them is scammy or weird.
“It’s important to note that Facebook is Meta now, but the metaverse play has really fizzled. They don’t know what the future is, but they do know that ‘Facebook’ is absolutely not the future,” Roberts said. “So there’s a level of disinvestment in Facebook because they don’t know what the next thing exactly is going to be, but they know it’s not going to be this. So you might liken it to the deindustrialization of a manufacturing city that loses its base. There’s not a lot of financial gain to be had in propping up Facebook with new stuff, but it’s not like it disappears or its footprint shrinks. It just gets filled with crypto scams, phishing, hacking, romance scams.”
“And then poor content moderation begets scammers begets this useless crap content, AI-generated stuff, uncanny valley stuff that people don’t enjoy and it just gets worse and worse,” Roberts said. “So more of that will proliferate in lieu of anything that you actually want to spend time on.”
The five-time champion’s lawyer says the cyclist has lost ‘absolutely everything’ and ‘doesn’t have an address’

Cate Blanchett’s claim to be ‘middle class’ isn’t unique among the wealthy, or even the 1% she’s part of. Downplaying privilege among elites contributes to the problem of wealth inequality.

The free ecoSwitch app takes the guesswork out of sustainable food choices, empowering consumers to take matters into their own hands.

Every time I talk about privacy online, the pessimists always come out. "It's impossible to have any online privacy." "They've already collected so much data about you. Why bother?" Is it really well and truly over? Or are there actually good reasons to still care about online privacy in the age of ...

In sharing this video here I'm preaching to the choir, but I do think it indirectly raised a valuable point which probably doesn't get spoken about enough in privacy communities. That is, in choosing to use even a single product or service that is more privacy-respecting than the equivalent big tech alternative, you are showing that there is a demand for privacy and helping to keep these alternative projects alive so they can continue to improve. Digital privacy is slowly becoming more mainstream and viable because people like you are choosing to fight back instead of giving up.
The example I often think about in my life is email. I used to be a big Google fan back in the early 2010s and the concept of digital privacy wasn't even on my radar. I loved my Gmail account and thought it was incredible that Google offered me this amazing service completely free of charge. However, as I became increasingly concerned about my digital privacy throughout the 2010s, I started looking for alternatives. In 2020 I opened an account with Proton Mail, which had launched all the way back in 2014. A big part of the reason it was available to me 6 years later as a mature service is because people who were clued into digital privacy way before me chose to support it instead of giving up and going back to Gmail. This is my attitude now towards a lot of privacy-respecting and FOSS projects: I choose to support them so that they have the best chance of surviving and improving to the point that the next wave of new privacy-minded people can consider them a viable alternative and make the switch.
Children are gathering large followings and earning thousands of dollars through social media influencing — but some warn it comes with a dark side.

I stumbled across this today and thought it was worth sharing. I have used every one of these ROMs except /e/ and they are all good projects in their own right.
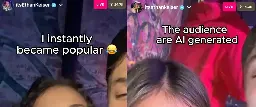
"I downloaded this app called Parallel Live which makes it look like you have tens of thousands of people watching. Instantly, I became the life of the party."
A market for manipulating Reddit using AI have emerged.

Even in states that don’t have daylight saving, most people favour it. However, support is strongest in the country’s south, where the difference between summer and winter daylight hours is greater.

Cafe owners have tried to keep prices low but are being squeezed out by tight margins.

Politicians are all too aware that a metaphorical poverty freight train is coming for a generation of renters, but can a collision be avoided, asks David Taylor.

Coles plans to ‘optimise its workforce’ with big data and AI tools from a controversial tech company.

